Science
A world-class platform based on world-class science.
Site-specific protein conjugation – through the power of synthetic biology
By expanding the genetic code to use more than the 20 natural amino acids, we are able to place synthetic bio-orthogonal chemical handles into a protein. The video below demonstrates this approach.
Genetic code expansion and synthetic amino acid incorporation
Our technology completely frees up one codon of the genetic code to be used by our proprietary synthetic amino acid with no loss in expression system viability or yield.
1. A proprietary engineered tRNA-synthetase charges our synthetic amino acid onto its cognate tRNA

2. The tRNA is shuttled to the ribosome and reads the freed up codon. The ribosome incorporates our synthetic amino acid into the growing polypeptide chain.
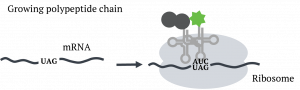
3. The polypeptide chain containing one or multiple synthetic amino acids folds into its 3D structure to give a synthetic protein ready for site-specific conjugation

Our science, your benefit.
Partnering
Find out more how we can support you in developing cutting-edge biologics.
Learn more